KARST /LIMESTONE REGION
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIMESTONE REGION
Karst regions are characterized by distinctive geological and topographical features, which are primarily formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, usually limestone or dolomite. Some of the key features of karst regions include:
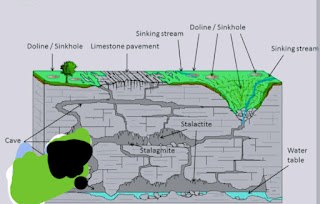
1. **Sinkholes**: Sinkholes are depressions or holes in the ground that form when the underlying soluble rock
These features make karst regions not only geologically fascinating but also visually striking. They are known for their rugged and unique landscapes, often with a complex network of underground features and surface formations. Sinkholes are depressions or holes in the ground that form when the underlying soluble rock dissolves and creates voids. They can be small or large and are a common feature of karst landscapes.
dissolves and creates voids. They can be small or large and are a common feature of karst landscapes.
2. Caves: a caves is a large underground chamber which has a connecting Shaft to the surface. The usually occur above water table and caused by the widening of limestone lines of weakness such as joints, fissure and bedding. While a Carven is a larger form of cave and may have two or more levels to form a Carven. Karst regions often contain extensive cave systems, which are formed as water seeps into the ground and dissolves the rock, creating underground passages and chambers.
4. **Poljes**: Poljes are large, flat-bottomed depressions or valleys in karst landscapes, often surrounded by hills or ridges. They can become flooded during heavy rains.
5. **Cenotes**: Cenotes are natural sinkholes or water- filled pits that provide access to underground aquifers. They are common in karst regions, especially in places like the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
6. **Resurgence Springs**: Resurgence springs, also known as karst springs, are where underground rivers and streams re-emerge at the surface. They are often a source of freshwater in karst regions.
7. **Karren**: Karren, or limestone pinnacles, are small-scale, weathered limestone features that result from the dissolution of the rock. They can give a distinctive appearance to the landscape.
8. **Dolines**: Dolines are funnel- shaped depressions that form when the roof of a cave or underground cavity collapses. They can vary in size and shape. and may vary in size. Which are gradually enlarged through continue dissolution.
9. **Underground Rivers**: Karst regions often have extensive underground river systems that flow through caves and cavities, creating unique hydrological networks.
10. **Karst Lakes**: Karst lakes are typically found in dolines or sinkholes and may vary in size. They often have a transparent, blue colour due to the filtration of water through the limestone.
These features make karst regions not only geologically fascinating but also visually striking. They are known for their rugged and unique landscapes, often with a complex network of underground features and surface formations
EXAMPLES OF KARST REGION AROUND THE WORD
Here are some examples of karst regions around the world:
1. **Krabi, Thailand**: Krabi province in southern Thailand is known for its stunning karst landscapes, particularly in places like Railay Beach and Ao Nang.
2. **Guilin, China**: The karst hills along the Li River in Guilin are iconic and have been depicted in many Chinese paintings.
3. **Waitomo, New Zealand**: The Waitomo Caves in New Zealand are famous for their limestone formations, including glowworm caves.
4. **Burren, Ireland**: The Burren in County Clare is a unique karst landscape with limestone pavements, caves, and underground rivers.
5. **Mammoth Cave, Kentucky, USA**: Mammoth Cave National Park is home to the longest cave system in the world, formed in a karst region.
6. **Jura Mountains, France and Switzerland**: This mountain range features extensive karst formations, including limestone plateaus and sinkholes.
7. **Phong Nha-Ke Bang, Vietnam**: This national park is known for its karst landscapes and contains some of the world's largest caves, including Son Doong Cave.
8. **Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico**: The Yucatan Peninsula is riddled with cenotes, sinkholes, and underground rivers formed in the karst terrain.
9. **Slovenian Karst, Slovenia**: This region in Slovenia is known for its limestone caves, with Postojna Cave and Škocjan Caves being prominent examples
10. **Gunung Mulu National Park, Malaysia**: This UNESCO World Heritage site in Borneo features karst formations, extensive cave systems, and unique limestone pinnacles.
11.** Silver Spring, Florida. USA
12.** Ingleborough District of Yorkshire in England where gaping Ghyll is an example of swallow holes.
13.** Malambolo Gorge of Madagascar
14.** The Congo caves at the foot of Cape Ranges in South Africa.
15,** Karst regions are characterized by unique landscapes formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks like limestone or dolomite. In Africa, the most well-known karst region is the **Tassili n'Ajjer** in Algeria. It features dramatic rock formations, caves, and rock art.
Karst regions in Nigeria are primarily associated with limestone formations and feature distinctive landscapes. Some notable karst areas in Nigeria include:
1. **Obudu Plateau:** Located in Cross River State, the Obudu Plateau is known for its limestone formations and stunning landscapes. The plateau is a popular tourist destination and is characterized by its lush vegetation and unique geological features.
2. **Mambilla Plateau:** Situated in Taraba State, the Mambilla Plateau also exhibits karst topography with limestone outcrops. It is known for its cool climate, scenic beauty, and agricultural activities.
3. **Awe and Awgu Plateaus:** These plateaus in Nigeria also have karst features, including limestone formations.
4.** Okpella in Edo state, have lime stone formations.
These karst regions in Nigeria are not only geologically interesting but are also important for agriculture and tourism. They offer picturesque landscapes and potential for various outdoor activities.
These are just a few examples of karst regions found in different parts of the world, each with its unique geological and natural features.







Comments
Post a Comment