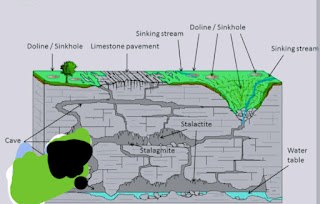
CLASSIFICATION OF CLIMATE
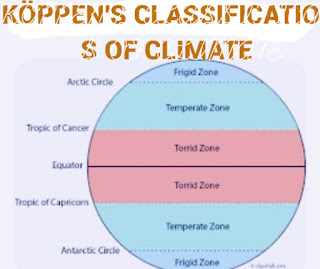
Köppen's classification of climate, also known as the Köppen-Geiger climate classification system, was first introduced by the German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and later modified by Rudolf Geiger. It is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It categorizes the world's climates based on average temperatures, precipitation, and sometimes seasonal patterns. The system uses a series of letters to denote the main climate types, with further subdivisions based on more specific criteria. The main climate types are: 1. A - Tropical/megathermal climates: Climates with an average temperature above 18°C (64.4°F) in every month of the year and which may have significant rainfall. - Af: Tropical rainforest - Am: Tropical monsoon - Aw/As: Tropical savanna with dry winter/summer 2. B - Dry (arid and semi arid) climates: Climates cha...